Children with resonance disorders (hypernasality, hyponasality and cul de sac resonance) or velopharyngeal dysfunction can present challenges for speech-language pathologists (SLPs) in all settings. The purpose of this article is to present current, practical information for practicing SLPs who frequently or occasionally see individuals with a history of cleft palate or abnormal resonance.
Normal Resonance and Velopharyngeal Function
Resonance, as it relates to speech, is the modification of the sound that is generated by the vocal folds as it vibrates (resonates) through the cavities of the vocal tract (pharynx, oral cavity, and nasal cavity). The type and quality of resonance is determined greatly by the function of the velopharyngeal valve. As shown in Figure 1, the velopharyngeal valve is open for nasal breathing and remains open for the production of nasal sounds (m, n, L).
Figure 1. Velum at Rest during Normal Nasal Breathing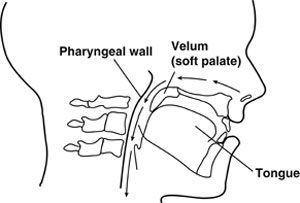
From Cleft Palate and Craniofacial Anomalies Effects on Speech and Resonance (2nd ed.) by A. Kummer, 2008. Reprinted with permission of Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning: www.thomsonrights.com. Fax 800-730-2215.
When oral sounds are produced during speech, the velopharyngeal valve closes, thus directing both sound energy and airflow from the pharynx into the oral cavity (see Figure 2). Because airflow and sound travel in a superior direction from the lungs to the oropharynx, the velopharyngeal valve must close completely to prevent speech distortion.
Figure 2. Velum Elevated to Achieve Velopharyngeal Closure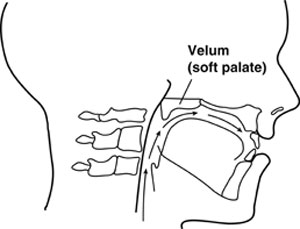
From Cleft Palate and Craniofacial Anomalies Effects on Speech and Resonance (2nd ed.) by A. Kummer, 2008. Reprinted with permission of Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning: www.thomsonrights.com. Fax 800-730-2215.
Resonance Disorders & Velopharyngeal Dysfunction: Simple Low-Tech and No-Tech Procedures for Evaluation and Treatment
December 10, 2007
Related Courses
1
https://www.speechpathology.com/slp-ceus/course/20q-evaluation-and-treatment-speech-8729
20Q: Evaluation and Treatment of Speech/Resonance Disorders and Velopharyngeal Dysfunction
Children with speech and resonance disorders (hypernasality, hyponasality, and cul-de-sac resonance) and/or nasal emission present challenges for speech-language pathologists (SLPs) in all settings. This article will help participants to recognize resonance disorders and the characteristics of velopharyngeal dysfunction, and provide appropriate management.
textual, visual
129
USD
Subscription
Unlimited COURSE Access for $129/year
OnlineOnly
SpeechPathology.com
www.speechpathology.com
20Q: Evaluation and Treatment of Speech/Resonance Disorders and Velopharyngeal Dysfunction
Children with speech and resonance disorders (hypernasality, hyponasality, and cul-de-sac resonance) and/or nasal emission present challenges for speech-language pathologists (SLPs) in all settings. This article will help participants to recognize resonance disorders and the characteristics of velopharyngeal dysfunction, and provide appropriate management.
8729
Online
PT60M
20Q: Evaluation and Treatment of Speech/Resonance Disorders and Velopharyngeal Dysfunction
Presented by Ann W. Kummer, PhD, CCC-SLP
Course: #8729Level: Intermediate1 Hour
ASHA/0.1 Intermediate, Professional; Calif SLPAB/1.0; IACET/0.1; Kansas LTS-S1370/1.0; SAC/1.0
Children with speech and resonance disorders (hypernasality, hyponasality, and cul-de-sac resonance) and/or nasal emission present challenges for speech-language pathologists (SLPs) in all settings. This article will help participants to recognize resonance disorders and the characteristics of velopharyngeal dysfunction, and provide appropriate management.
2
https://www.speechpathology.com/slp-ceus/course/sound-judgment-speech-prerequisites-therapy-10447
Sound Judgment: Speech Prerequisites, Therapy Techniques, and Use of Motor Learning Principles
Differentiating obligatory distortions from compensatory productions, sensory feedback techniques, and effective placement strategies for correction of speech sound errors (e.g., lateral lisp and distortion of /ɚ/ and /r/) are described in this course. Motor learning and motor memory principles are discussed as a framework for achieving carryover after sound acquisition has occurred.
auditory, textual, visual
129
USD
Subscription
Unlimited COURSE Access for $129/year
OnlineOnly
SpeechPathology.com
www.speechpathology.com
Sound Judgment: Speech Prerequisites, Therapy Techniques, and Use of Motor Learning Principles
Differentiating obligatory distortions from compensatory productions, sensory feedback techniques, and effective placement strategies for correction of speech sound errors (e.g., lateral lisp and distortion of /ɚ/ and /r/) are described in this course. Motor learning and motor memory principles are discussed as a framework for achieving carryover after sound acquisition has occurred.
10447
Online
PT90M
Sound Judgment: Speech Prerequisites, Therapy Techniques, and Use of Motor Learning Principles
Presented by Ann W. Kummer, PhD, CCC-SLP, ASHA Fellow
Course: #10447Level: Intermediate1.5 Hours
AG Bell - LSLS/1.5 Domain 3; ASHA/0.15 Intermediate, Professional; Calif SLPAB/1.5; IACET/0.2; Kansas LTS-S1370/1.5; SAC/1.5
Differentiating obligatory distortions from compensatory productions, sensory feedback techniques, and effective placement strategies for correction of speech sound errors (e.g., lateral lisp and distortion of /ɚ/ and /r/) are described in this course. Motor learning and motor memory principles are discussed as a framework for achieving carryover after sound acquisition has occurred.
3
https://www.speechpathology.com/slp-ceus/course/causes-and-characteristics-resonance-disorders-7915
Causes and Characteristics of Resonance Disorders and Velopharyngeal Dysfunction, presented in partnership with Cincinnati Children's
This is Part 1 of a two-part series. Children with resonance disorders (hypernasality, hyponasality and cul-de-sac resonance) or suspected velopharyngeal dysfunction present challenges for SLPs in all settings. This course is designed to provide information about the causes and characteristics of resonance disorders and velopharyngeal dysfunction so that these disorders can be recognized and appropriate treatment can be recommended.
auditory, textual, visual
129
USD
Subscription
Unlimited COURSE Access for $129/year
OnlineOnly
SpeechPathology.com
www.speechpathology.com
Causes and Characteristics of Resonance Disorders and Velopharyngeal Dysfunction, presented in partnership with Cincinnati Children's
This is Part 1 of a two-part series. Children with resonance disorders (hypernasality, hyponasality and cul-de-sac resonance) or suspected velopharyngeal dysfunction present challenges for SLPs in all settings. This course is designed to provide information about the causes and characteristics of resonance disorders and velopharyngeal dysfunction so that these disorders can be recognized and appropriate treatment can be recommended.
7915
Online
PT90M
Causes and Characteristics of Resonance Disorders and Velopharyngeal Dysfunction, presented in partnership with Cincinnati Children's
Presented by Ann W. Kummer, PhD, CCC-SLP
Course: #7915Level: Intermediate1.5 Hours
ASHA/0.15 Intermediate, Professional; Calif SLPAB/1.5; IACET/0.2; Kansas LTS-S1370/1.5; SAC/1.5
This is Part 1 of a two-part series. Children with resonance disorders (hypernasality, hyponasality and cul-de-sac resonance) or suspected velopharyngeal dysfunction present challenges for SLPs in all settings. This course is designed to provide information about the causes and characteristics of resonance disorders and velopharyngeal dysfunction so that these disorders can be recognized and appropriate treatment can be recommended.
4
https://www.speechpathology.com/slp-ceus/course/evaluation-speech-resonance-disorders-secondary-7916
Evaluation of Speech/Resonance Disorders Secondary to Velopharyngeal Dysfunction, presented in partnership with Cincinnati Children's
This is Part 2 of a two-part series. Children with resonance disorders (hypernasality, hyponasality and cul-de-sac resonance) present challenges for speech-language pathologists (SLPs) in all settings. This course is designed to provide simple, yet very reliable low-tech evaluation techniques for practicing SLPs who frequently or occasionally see clients with cleft palate, hypernasality, or suspected velopharyngeal dysfunction. (Part 1: Course 7915)
auditory, textual, visual
129
USD
Subscription
Unlimited COURSE Access for $129/year
OnlineOnly
SpeechPathology.com
www.speechpathology.com
Evaluation of Speech/Resonance Disorders Secondary to Velopharyngeal Dysfunction, presented in partnership with Cincinnati Children's
This is Part 2 of a two-part series. Children with resonance disorders (hypernasality, hyponasality and cul-de-sac resonance) present challenges for speech-language pathologists (SLPs) in all settings. This course is designed to provide simple, yet very reliable low-tech evaluation techniques for practicing SLPs who frequently or occasionally see clients with cleft palate, hypernasality, or suspected velopharyngeal dysfunction. (Part 1: Course 7915)
7916
Online
PT90M
Evaluation of Speech/Resonance Disorders Secondary to Velopharyngeal Dysfunction, presented in partnership with Cincinnati Children's
Presented by Ann W. Kummer, PhD, CCC-SLP
Course: #7916Level: Intermediate1.5 Hours
ASHA/0.15 Intermediate, Professional; Calif SLPAB/1.5; IACET/0.2; Kansas LTS-S1370/1.5; SAC/1.5
This is Part 2 of a two-part series. Children with resonance disorders (hypernasality, hyponasality and cul-de-sac resonance) present challenges for speech-language pathologists (SLPs) in all settings. This course is designed to provide simple, yet very reliable low-tech evaluation techniques for practicing SLPs who frequently or occasionally see clients with cleft palate, hypernasality, or suspected velopharyngeal dysfunction. (Part 1: Course 7915)
5
https://www.speechpathology.com/slp-ceus/course/20q-ankyloglossia-myths-and-evidence-10990
20Q: Ankyloglossia - Myths and Evidence Regarding Its Effects on Function
There is much controversy about the diagnosis of ankyloglossia and its potential effects on neonatal feeding and speech. Guidance regarding the diagnosis of ankyloglossia and a summary of current research regarding its potential effects on function are provided in this course.
textual, visual
129
USD
Subscription
Unlimited COURSE Access for $129/year
OnlineOnly
SpeechPathology.com
www.speechpathology.com
20Q: Ankyloglossia - Myths and Evidence Regarding Its Effects on Function
There is much controversy about the diagnosis of ankyloglossia and its potential effects on neonatal feeding and speech. Guidance regarding the diagnosis of ankyloglossia and a summary of current research regarding its potential effects on function are provided in this course.
10990
Online
PT60M
20Q: Ankyloglossia - Myths and Evidence Regarding Its Effects on Function
Presented by Ann W. Kummer, PhD, CCC-SLP, ASHA Fellow
Course: #10990Level: Intermediate1 Hour
ASHA/0.1 Intermediate, Professional; Calif SLPAB/1.0; IACET/0.1; IL EITP/1.0; Kansas LTS-S1370/1.0; SAC/1.0
There is much controversy about the diagnosis of ankyloglossia and its potential effects on neonatal feeding and speech. Guidance regarding the diagnosis of ankyloglossia and a summary of current research regarding its potential effects on function are provided in this course.

