Question
As a speech pathologist, I routinely come across reports documenting tympanogram results. Can you run down the list of common tympanogram types?
Answer
To understand the types of tympanograms, you should first understand the meaning behind the parts of the graph itself. A tympanogram provides information regarding the compliance of the middle ear system (how well sound passes through the eardrum to the middle ear system), ear canal volume, and middle ear pressure. Compliance is plotted vertically on the tympanogram, and is measured in ml or mmho. Maximum compliance of the middle ear system occurs when the pressure in the middle ear cavity is equal to the pressure in the external auditory canal. This compliance (static acoustic admittance) is represented by the highest peak of the curve on the graph (Figure 1). Pressure is indicated on the horizontal axis of the graph, and is measured in decaPascals.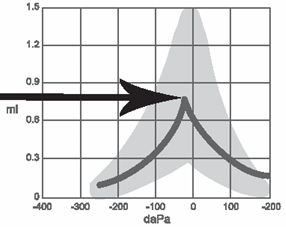
Figure 1. Tympanogram showing maximum peak compliance.
The classification system for tympanograms commonly used today was developed by Liden (1969) and Jerger (1970). There are three main types of tympanograms: A, B, and C. Type A tympanograms look like a teepee, and indicate a normal middle ear system, free of fluid or physiological anomalies which would prevent the admittance of sound from the middle ear into the cochlea. Figure 1 shows an example of a Type A tympanogram.
Type B tympanograms are a flat line (Figure 2), which is consistent with middle ear pathology, such as fluid or infection behind the ear drum. In some cases, these tympanograms are seen when there is a hole in the ear drum; the difference lies in the ear canal volume: a larger ear canal volume indicates a perforation in the ear drum.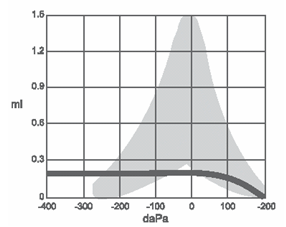
Figure 2. Type B tympanogram
Type C tympanograms (Figure 3) are still shaped like a teepee, but are shifted negatively on the graph. This indicates negative pressure in the middle ear space, often consistent with sinus or allergy congestion, or the end-stages of a cold or ear infection.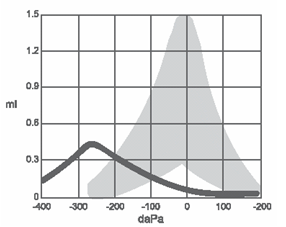
Figure 3. Type C tympanogram
References
Jerger, J.F. (1970). Clinical experience with impedence audiometry. Archives of Otolaryngology, 92, 311-324.
Liden, G. (1969). The scope and application of current audiometric tests. Journal of Laryngology and Otology, 83, 507-520.
Jen Duffey, M.S., CCC-A has been an audiologist for Maico-Diagnostics (www.maico-diagnostics.com) for three years. She provides audiological support and education, input for new product design and function, and technical assistance. Previously, she worked for three years as an educational audiologist providing clinical services to students, ages 2 to 21 years old.
